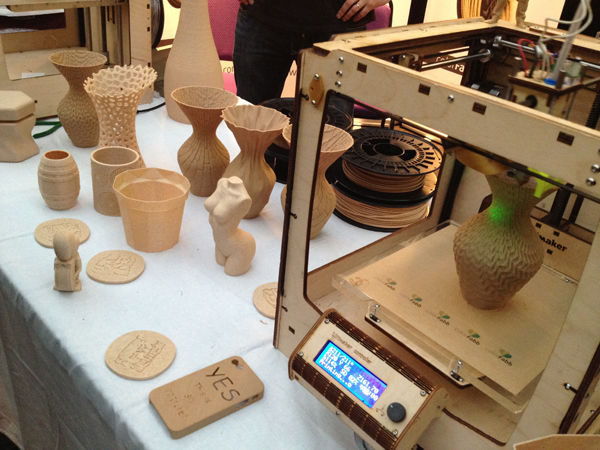
Starting to work with 3D printing can be challenging. With so many materials and technologies available, creating a budget seems impossible. But don’t worry! If you can’t find the answer to “How much does 3D printing cost?”, we can help!
There are a lot of factors to consider when it comes to 3D printing. Basically, printing in 3D can cost between $30 to thousands of dollars. What you need to consider is: what kind of materials will be used, the complexity of the model, and the labor included in the process. The last one is tricky since the service of 3D printing can sometimes cost more than an actual 3D printer, making it so it would be easier if you printed your designs yourself.
We’ll explain all the details in this article. Let’s do it step by step.
First, we’ll explain the factors that affect the price when it comes to the 3D model you want to print. Those are the same regardless if you are using a service of 3D printing or printing it yourself.
3D model
The size, complexity, and volume of the model are some of the main things that vary the 3D printing cost.
As the logic goes, the bigger the model in size, the more expensive it is. Generally, that does apply, but the key in this scenario is the density. When you increase the density, you increase the amount of material used to create your model. Therefore, the price is also increased.
Following this line of thought, a model that is 3ft in size can have less volume than one measuring 1ft. That’s because if the 3ft one is hollow, and the 1ft is solid, the last one has a larger volume and uses more material.
So, here’s a tip! If you’re looking to reduce your 3D printing cost, consider making your models hollow. That, of course, if your project doesn’t require strong, solid models.
Another factor that determines the price is the complexity of the model. That’s because not all models are created the same way. Actually, almost none of them are. The beauty of 3D printing is that, as the technologies develop, you can print pretty much anything. On the other hand, that makes calculating the 3D printing cost even harder since each product can be very unique.
For certain situations, not even the most complex algorithms can calculate the 3D printing costs. Sometimes, only a human perspective can analyze the price and viability of a project. For simpler products, though, the printing can be automated, which makes calculating the 3D printing cost easier.
With the basics of the model covered, let’s move to another factor. Once you have the size, volume, and complexity of your model decided, the next spet is choosing the material. The more expensive the material, the higher the 3D printing cost.
Type of Materials
Thermoplastics: Filaments and Powders

When it comes to 3D printing materials, the cheapest kinds are thermoplastics. Even if you are new to the 3D printing field, you must have heard of “ABS” or “PLA”. That is because they are the most widely used material in 3D printing, which makes them less expensive. Loved by hobbyists and beginners, the materials can cost from $20 to $70 per kg.
Another thermoplastic well used is the nylon powders. Coming in the polymers Nylon PA11/12, Nylon PA12, Nylon 3200 Glass-filled, the price stays around tens of dollars per kg.
Even though the materials are cheap, the resulted product doesn’t have the highest quality. In this case, thermoplastic materials are mostly indicated for prototyping applications instead of the final product since the result won’t come with many details and is low quality. Plus, it’s almost impossible to print a very complex model with this kind of material, even if you do finishing touches.
So, even though using filaments and powders as your material can lower your 3D printing cost, make sure you’re using them for proper scenarios.
Thermosets: Resins

This material is the most indicated for big and complex 3D printing projects. Resins are a more technological material and can provide a way higher quality than thermoplastics. But, the thing with 3D printing materials is, the higher the quality and technology provided, the more expensive.
The most standard resin costs about $50 per liter, which can fit into thermoplastics costs. But, some resin materials can cost up to $300 per liter. The good news is that 3D printing companies can usually get discounts and pay lower prices for this kind of material.
Metals

The most expensive materials for 3D printing are metals. Used in specific kinds of technologies, metals like Aluminum AlSi7Mg0,6 and Stainless Steel 316L can cost hundreds of dollars per kilo.
If you want to understand the materials available for 3D printing in a more detailed way, check this article out!
But, regardless of the kind of material you choose to use when it comes to 3D printing, you need to consider the need for finishing touches and the cost of those post-processing techniques.
Post-processing
What most don’t realize and end up not adding to 3D printing costs is the finishing touches the models require. 3D printing is not an instant process and goes beyond simply designing and printing.
The resulted print needs to be cleaned, curated, and polished before being ready to use. That applies especially to more complex designs that a raw texture can ruin.
Polishing
When it comes to filaments, printing a model that needs polishing is just a waste of time. The pieces come out too raw, and even if you do waste hours and money sanding the prints, the quality of the final product wouldn’t even compare to resin.
If you print it in resin, the process is simpler. Since the pieces are UV cured, it’s easier to polish them using a sandblaster or even by hand.
Once again, these pieces of information prove how much the model you’re printing matters when it comes to 3D printing costs. There are some models that are so complex that the generated models are almost impossible to clean. And, if you don’t properly clean the pieces, they won’t look as good and could even not work as they should, affecting your whole project.
Finishing
Most printing technologies available right now don’t allow you to add customized colors to your 3D prints. So, if you want to dye or paint (the most expensive one) the 3D models you print with different colors, you are going to need to do it after the product is already printed. All that adds to the final cost since it requires equipment and a workforce.
Now that you understand mostly everything regarding the model, you must be wondering: how do I design it? Here are your options.
Design
The amount you spend to design your model can vary greatly, depending on the option you choose. You can have a freelancer design it for you, buy your own CAD software to make it yourself, or even get your model on a free 3D model Database if you don’t need anything customized. In any way, your design will determine mostly all your other 3D printing costs. That’s because it’s through the design that you can establish your model’s size, volume, and complexity, leading to higher or lower costs. Plus, it will define the thickness of your walls, if your project has any, and how dense your parts will be.
Remember the tip from the beginning of the article? Even though hollowing parts significantly lowers the 3D printing cost, that technique requires high skills. Plus, you need to know and understand your file well to determine if making a part hollow will affect your whole project. In cases like this, considering hiring a professional to make your design instead of trying to make it yourself might be the best option.
On the other hand, if you’re creating simpler models, or just a prototype, downloading or buying a CAD software can be a great alternative. This option can help you lower the 3D printing cost and can even improve your designing skills.
In any way, if you’re hiring a service or providing the service yourself, you need to understand the profit margins involved in the process.
Profit Margins
Profit Margins exist to keep a company running. As we explain throughout the article, there are many costs to 3D printing that goes beyond the printer itself. In the 3D printing business, the profit margins can be between 50% to 90%, based on material cost. If you include labor and overhead costs, the profit margin does decrease a lot, but it makes the calculation more complex.
Another thing to consider is the base price or minimum fee. This cost is added if the product you’re printing in a company costs less than a certain amount. If material-wise, your product costs $5, and that’s all the company charger, they’re losing money. That’s because, as we learned, the cost of 3D printing goes beyond the material.
Even if the service is highly automated, there is still labor involved. In these cases, you pay the base price, which is around $30 to $90.
Let’s move to the more technical parts and understand the costs of 3D printers and their operations.
3D printer costs

There are very different technologies of 3D printers available on the market. You can get simple machines for around $200 and more sophisticated ones for a price that can go up to tens of thousands of dollars. If you’re considering buying your own printer, you have to understand which technology suits your needs better.
The main features you need to look at when choosing which 3D printer to buy are size, speed, precision, and, the most important one, the technology it uses. The last one will define the materials that you will be able to use and, of course, the more advanced the technology, the higher the price of the printer. So, you should ask yourself, “what exactly am I trying to achieve with this printer?”.
FDM technology
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is the cheapest and simplest technology of 3D printing available. If you’re looking to initiate in the 3D printing technology and experiment with it, you can get an FDM 3D printer for about $200. What you need to keep in mind is that this kind of printer isn’t the fastest and can’t print in the thinnest, most accurate pieces. Being a low-range printer, FDMs are great to get you started at a low cost.
This technology isn’t made for long producing processes and can lead to frequent breakdowns if put through it. In this case, considerer getting this printer if you don’t need fast and high-quality products.
Also, you should keep in mind that this kind of printer doesn’t support certain materials, like resin. Like mentioned before, the materials used in the FDM technology are the simpler ones, the thermoplastics.
Advanced technologies
As the logic goes, the prices of 3D printers go up as the technologies used by the printers advance. The most used technology by professionals is Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), and printers that use can cost up from $5,000. Even though this technology is way more expensive than FDM, it can print more complex objects, and it is way faster.
This kind of printer works well with resins and makes it possible to finish the product. But, getting a high-end, more expensive printer depends on how much you’ll use it. If you plan on printing just one project or one-offs piece, getting your own 3D printer may not be worth it. 3D printing services might be the better solution in this scenario.
3D printing services
Now that you understand the 3D printing cost better, it should be clearer which is the best path to follow. But, one last thing you shouldn’t leave aside is the cost of 3D printing services, which can make your life easier, depending on what you need to print.
Here’s what you need to check before you choose a 3D printing service:
- Which materials are available in their service and if they have the one you need, or something close to it;
- Their ability to handle batch production, so you can see if they can meet your demands;
- How long they take to print. Sometimes a company charges less for the service but takes longer to get it done, which can delay your project.
After you found a company that fits your needs, here are some tips to pre-calculate the 3D printing cost beforehand, on your own.
Companies charge mostly on top of the materials, as we explained before. Usually, they have a list of how much they charge for each material. To calculate, all you have to do is multiply the cost of the material you need by the volume of your 3D file.
Besides that, they charge on top of manual labor (which goes under service fee), maintenance cost (which is usually covered by the base price or minimum fee), and the layer height (the bigger the number of layers, the more expensive the production), resolution and time to print.