3D printing continues to advance. One of the current questions is whether this technology will assist us in repairing damages caused to nature during centuries or create even more. Can eco-friendly 3D printing be something feasible, or is it something that might not happen for a while?
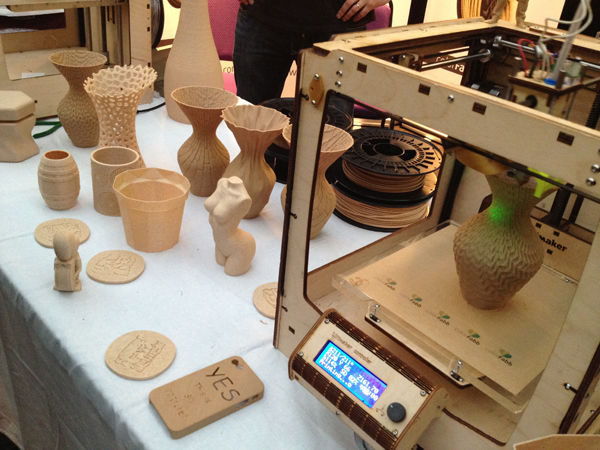
When people in a long past pictured what 2020 would be like, most certainly, they predicted flying cars and home machines that give them everything they wanted by pressing a button. Even though we do not have flying cars yet, we are each day closer to printing anything we want. 3D printing is the use of filaments, powder, and other kinds of material to create objects from scratch.

3D printing surely is an innovative form of making objects, as it is simple and can be done even at home if you have the correct tools. The possibilities are endless: figurines, devices, objects, appliances, and even houses were 3D printed. For example, medical engineers have likewise developed a bio-ink that has human cells integrated into it. They are studying the possibility of printing human organs, such as noses, ears, and even a heart with every part of it – veins, arteries, and such.
Bioprinters have been 3D printing minor sizes of human organs, such as brains and kidneys, so researchers can study them better without using mice or other animals. Recently, researchers have made human-sized ears, bone, and muscle tissues from 3D printing using biomatter. They included human cells on their 3D printing, also using some bioplastic molds to receive them. Those cells rearranged themselves in a way they would not need that mold in a matter of time. Further, they implanted those parts in laboratory animals. They discovered the tissues found a way to grow veins, nerves, and even cartilage or bone cells. However, they do not know yet if those tissues will work on human bodies.

As you can see, you can print basically everything. It is possible to 3D print clothes, jewelry, accessories, nails, and more in the fashion industry. For those who are looking for fun, 3D printing can become a hobby. Some people print action figures, dolls, aircraft, or 3D print car parts as well. And it does not need to be in plastic. Many other options of material can be used to 3D print something. Even food can be printed!
Is 3D printing eco-friendly?
3D printing is real, and it is becoming more popular, as its price is reducing in the market. There are affordable smaller 3D printers that can be used at home. However, as it is a form of manufacturing, it is crucial to think about 3D printing effects on our environment, considering our planet’s current pollution situation.
The two prime materials used for 3D printing, when it comes to plastic filaments, are ABS and PLA. Both of them are thermoplastics, which means they are melted and molded. While ABS is made from petroleum, PLA comes from renewable materials such as corn-starch or sugarcane. For 3D printing, we call those plastic filaments or other material as ink. Though it is not literally a liquid written on something, the thread is melted and pushed into a surface, creating an ultrathin layer that solidifies pretty quickly. On top of that layer, another is made, and it goes on until the project is finished, which is why it is called additive manufacturing.

From the two options, PLA is more eco-friendly than ABS. ABS is made from petroleum, a long-lasting and less disposable option. There is biodegradable ABS plastic on the market, and it might be an answer to eco-friendly 3D printing; however, most of it is not recyclable. On the other hand, PLA is a bioplastic, which means it is made from compostable material. In other words, PLA is biodegradable. As it does not have toxic elements, PLA can be transformed into objects to contain food, for example. It takes less energy for it to become ink for 3D printers, and it generates less toxic fumes when printed. However, it is necessary to mention that PLA might not be your chosen material in some situations, as it can not handle high temperatures.
Considering those primary filaments used in 3D printing, it might seem that, in general, 3D printing is eco-friendly. However, it is necessary to think about what will happen to those materials once the printed object is no longer of use. PLA is the best option as it is recyclable, while ABS is mostly not, as mentioned above. Even though there is biodegradable ABS plastic, not every product made of it can be recycled.
A Dutch startup bought the idea of making recyclable filament made from recycled ABS and PET. This award-winning innovation came in hand as the thread is made mainly from plastic bottles and car dashboards. Those threads are free of toxic additives and are of high-quality plastic. Nevertheless, other startups aim to develop the same technology. There is a machine that creates ecological filaments from plastic waste, in a way that 3D printers can be more eco-friendly. For example, a gallon of milk can be transformed into 2.5 meters of 3D filament.
Coca-cola also launched a 3D filament made of twenty-five percent of recycled plastic bottles. Its goal is to inspire other influential companies and brands to use technology for a sustainable lifestyle. Furthermore, a couple of Swiss entrepreneurs launched a project to clean the beaches of France, Morrocco, and Spain by recycling plastic bottles, plugs, and other waste into filaments. Once ready, those filaments were transformed into 3D objects, which were sold on their website. They installed all the necessary equipment on a van in 2014 and drove from France to Morrocco, executing their project.

A very similar project aims to 3D print inexpensive prosthetic limbs from plastic waste found in beaches for children around the world. Billions of pounds of plastic are thrown to the ocean each year, something terrifying on a long shot. Those agencies, companies, non-profit, and volunteers collect plastic waste from the shores, and it is turned into 3D printing filaments. Those filaments are then printed into prosthetic limbs for children who do not have access to them, making their lives much more comfortable.
Thinking of other kinds of projects, Michelin is another company aiming to provide more sustainable products. It recently presented a prototype of a 3D printed tire – which is integrated with the wheel itself – entirely made from biosources and recycled tires. It is made of cardboard, used metals, tin cans, e-waste, plastic waste, tire chips, natural rubber, bamboo, paper, and orange zest. Their objective is to reduce the cars’ environmental footprints. Since it is airless, as its structure is inspired by corals and honeycombs, its advanced design is safer as it can not explode or blowout. Interesting, right?!

Talking about cars, a university in the Netherlands researched how to use eco-friendly 3D printing to build a car. Even though some manufacturers have developed cars more eco-friendly, like hybrid electric cars, fusing recycling to 3D printing was an ambitious project those students researched. Naming the vehicle Noah, the students modeled every part of it in a computer-aided-machine. Every piece was designed to be 3D printed with recycled materials, from chassis to external and internal components. The objective was to not only produce something essential to our daily lives but to make it environment-friendly. Besides recycling to create Noah, every part of it can be reused again when its lifecycle is over.
Besides eco-friendly threads made from recycled bottles and other kinds of plastics, 3D printing can be even cleaner. With the use of solar panels, it is possible to feed a 3D printer for about eight hours and have enough energy to work while recharging the next day. On the tests made, it was used plastic recycled from electronics (e-plastic), which comes from the carcass of notebooks and computers, phones, tablets, and even desktop telephones. So, in general, it is a much cleaner option because the objects made had less waste of materials, a clean source of energy, and the possibility of recycling the final product. Having a solar panel and the recycling of materials lower considerably 3D printing’s environmental footprint.
Although PLA is more eco-friendly than ABS, it is essential to note that it comes from vast farms of corn, soy, or other sources owned by huge companies. Most of them do not really care about having clean and eco-friendly policies and routines. Though they have segments on their companies that are directed to eco-friendly resources and products, other sections might be a bit aggressive to the planet. Some of these sections can be a severe font of pollution if not taken care of carefully. Furthermore, even though PLA is compostable, it might need commercial composting facilities to compost that kind of material. PLA needs specific heat and microbes to do the trick.
In conclusion, 3D printing using either of them is not entirely eco-friendly yet. Still, we are moving forward to other options for 3D printing to become a very better choice than industrial manufacturing.
What are these options?
Besides PLA and ABS, there are some other options for 3D printing that can be more eco-friendly. Startups and companies are developing filaments made of many sources, such as wood, clay, soy, algae, fungus, and many more.
Wood-like and clay-like filaments are made of a mixture of wood or clay with plastic, creating a final product that resembles those materials very similarly. It feels and looks like wood or clay. Those types of filaments can be composed up to 50% of the raw material, added to PLA. BambooFill, for example, is made fifty percent of bamboo and fifty percent of PLA.
Some researchers are developing a wood-like filament made of recycled wood. There is a massive amount of waste of material when companies produce furniture, and their objective is to direct that waste to something with value. That initiative has relevant potential for the environment, as it can reduce waste/garbage and unclean wood exploitation.

Furthermore, a Dutch startup created a filament made of algae mixed with PLA, which is an up-and-coming option for eco-friendliness, possibly replacing synthetic plastic in the long run. They cultivate algae, then let them dry completely to process it to PLA. That algae grow absorbing carbon and leaving a starch that can be used as raw material for bioplastics, and the waste is only air. That biomatter can be used to build many objects, like shampoo bottles or even tables.
There are also filaments made of waste from processes of roasting coffee, industrial hemp, and even beer. As mentioned before, other materials such as cardboard, paper, tin cans, insect carcasses, and many more can be used to be recycled and added to filaments.
Researchers in Europe have been studying the possibility of using food waste as a bio-additive to create bio-filaments. They added extracts of lemon, lemon and almond peels, almond husks, pomegranate, and chemical enhancers to their PLA base. The result was a more robust filament that had higher heat tolerance. They could even add other properties like odor-giving or antibacterial properties.
Basically, anything organic or that is recyclable has the potential to become an eco-friendly filament. And, as mentioned, directing building objects with the usage of recycled waste is a much better option than the continuous usage of petro-plastic for our daily life.
Is 3D printing eco-friendly or not?
Although eco-friendly 3D printing is not entirely achievable at the present moment, some optimistic advances are being made in the industry. Choosing better materials for 3D printing, which can be the ones recycled or made of recycled plastic and content, can be an eco-friendly option. Compared to traditional manufacturing, it lowers carbon footprint considerably, also generates much less material waste, being a game-changer. United with cleaner sources of energy, 3D printing has the potential to revolutionize our lifestyle.
3D printing has its impact on the extraction of raw materials as well, considering its possibility of recycling what we already have in hands. It can lower, even more, the environmental pollution that happens in that process. The way industries are extracting petroleum for refining and creating resources from it is getting more aggressive every day. Our sources are becoming scarce. Not only that, but its maintenance, refining, and transportation is another subject when it comes to sources of pollution. It pollutes the air, the water, and the earth, especially when the product’s lifecycle comes to an end. Finding an eco-friendly option for manufacturing is becoming more of a matter of life and death each day.

3D printing can truly change the market. It can cause the rise of local commerce, as producers will be able to create personalized in-demand products according to their client’s needs. With faster 3D printers coming to the market, it can also impact the mass production of goods. Objects can be printed on-demand, reducing costs, waste of water and material, as the waste of other components. It potentially quickens production, having the potential of 3D printing big projects in a matter of hours. With models pre-designed, there will be no need to store vast amounts of products to be sold, but print them as they are made necessary. Not to mention that, along with those benefits, products can be enhanced and upgraded as 3D printing advances.
Nevertheless, there is one crucial aspect of 3D printing that must be reviewed and taken into consideration. It is the fact that for a cleaner lifestyle, companies should not direct their energies and resources into creating fields and fields of crops to generate more plastic. Neither should they use petro-plastic as the main component, as petroleum extraction is harmful to the environment. For 3D printing to be actually eco-friendly, those companies that make 3D printing filaments must recycle plastic and find other options to transform garbage into 3D printing threads.
Society, in general, daily generates tons and tons of garbage that could be recycled somehow. It is imperative to find a destination for many of those thrown-away objects and organic matter for constructing a better lifestyle. Being healthy does not only mean eating healthily, drinking water, and doing exercises. Being healthy means collaborating to a big-picture lifestyle that is conscious about our consumption of goods and how we generate waste and pollution. Being healthy means being mindful of how our actions impact the environment.

In that direction, researchers are coming up with ideas on how to create a better destination for the waste humankind generates. There are promising reports and articles about utilizing waste and organic matter to produce biodegradable bioplastics. As mentioned, billions of tons of garbage are thrown in the ocean daily. There is a prospection there is going to be more garbage than animals in the sea by 2050. And, none of our efforts for coming up with eco-friendly production methods matters if we continue to produce that amount of waste.
Considering it all, for 3D printing to become a 100% eco-friendly, some changes are needed to be done right now for impacting the big picture. However, for now, 3D printing is one of the best ways of consuming responsibly. It generates much less pollution, waste of material and resources, and 3D printing has clear potential to have a positive impact on the environment.
How can SolidFace help?
For anyone to 3D print anything, a computer-aided design (CAD) software is needed. SolidFace is the most complete CAD software out in the market, with great tools for those who desire to 3D print. SolidFace can aid you to design projects to be printed in an eco-friendly way.
We dramatically improve how you design and manufacture. SolidFace covers design, cost simulation, manufacturability checks, simulation, data management, collaboration, and sustainable design. Our CAD software helps you to develop your projects with a user-friendly interface, delivering a method of collaborating in real-time with your colleagues, teammates, or friends. It allows reducing costs and production time as you can see any changes made in the design right away.

SolidFace has a multi-purpose solution that enables you to share and create, edit, switch, or incorporate designs quickly, giving you much flexibility. All persons related to the project can access it from their own device as necessary, and it will be in your hands if they can edit it. Our solution tracks every move made, and you can access it easily.
Quality is one of our pillars, and SolidFace gives many tools to the user to develop designs and projects safely. Our integrated modules enable parts and subassemblies to be edited together, capturing design intent and making sure every piece is updated correctly. As the project is always up-to-date, everyone involved will be able to detect and correct possible errors, and it is recorded in real-time every editing. Do and undo as you will.
SolidFace has many advantages for your projects, and here are some of our leading features:
- Data management: we offer a built-in system of control and management to solve the costs of outsourcing it. Modifications are tracked, and any editing can be undone if necessary, and we provide a documented audit trail.
- Collaboration: simultaneously collaborate in projects with teammates or friends. SolidFace enables you to visualize any modification in real-time. Be able to add comments and assign tasks to keep everyone on the same page.
- 3D part library: SolidFace gives you access to an online part library with over a hundred million models from leading component manufacturers and distributors. Access thousands of standards, such as ISO, NF, GB, ASME, and many more.
- Parameterization: one of our leading features, it allows you to simulate motion simultaneously with the movement. SolidFace enables you to simulate 2D mechanisms either in the 2D drawing or 3D sketch module.
- Drawings: with our CAD, you can showcase details of your models with dimensions, datums, weld symbols, and surface finish, geometric tolerances, notes, tables, balloons, callout, sheets, and drawing properties. SolidFace supports the importation and exportation of DWG, DWT, and DXF formats.
SolidFace is your ally to create and design models as you need, with all the necessary tools for doing so. Let your creativity take you anywhere.