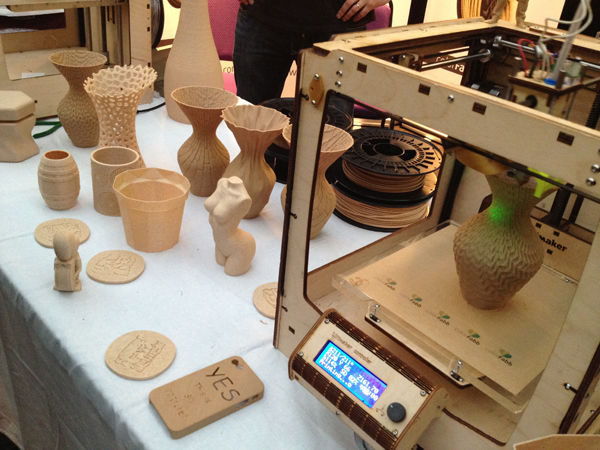
3D printing technologies are, most of all, a medium-term of the additive manufacturing (AM) process. Just for you know, AM is a technological improvement that transformed many analogic methods into a digital revolution during the last few years by the use of 3D CAD software along with a 3D Printer.
In this blog post, we will show you the ten 3D Printing technologies often used in industrial manufacturing:
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
- Stereolithography (SLA)
- Digital Laser Processing (DLP)
- Selective laser sintering (SLS)
- Direct metal laser sintering (DMLS)
- Drop on Demand (DOD)
- Material Jetting (MJ)
- Metal Binder Jetting (MBJ)
- Sand Binder Jetting (SBJ)
- Selective laser melting (SLM)
- Electron Beam Melting (EBM)
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
Among all 3D printing methods, it is the most economical technique but not recommended to handle complex projects. It is very advised to produce simple manufacturing projects with not so many details.
This technique consists of heating filaments of plastic material, usually PLA or ABS, to a semi-solid state and depositing it through the extruder nozzle. By moving it on the X, Y, Z axes, the object you want to obtain is formed layer by layer and solidifies once the printer filament cools down. The main advantage of this type of manufacturing over other types is the cost of material and the easiness to store and use. Also, this kind of process has more study material, and it suits a wide range of printers on the market, allowing from small entrepreneurs to large companies to have access to this technology.
In comparison to all the following types, FDM is more expensive than SLA and DLP.
Stereolithography (SLA)
This technique is remarkable for manufacturing pieces aiming for quality. Developed by Chuck Hull is the oldest technique among the types of 3D printing, being used until today.
It uses a laser and a reservoir with liquid resin. When the resin is hit by the laser in the contour relative to the shape of the object, that part “solidifies” and attaches to the bottom layer. Then, the support platform goes up or down, depending on the printer, a fraction of a millimeter in the tank. It allows the liquid resin to settle where the last layer of the solid part was. The laser process to restart until the piece to be completed.
Typically, this 3D printing technique must undergo both chemical and mechanical post-printing treatment to remove unwanted residues. Its main advantage is the possibility of manufacturing parts with a high degree of complexity and details, being widely used in dentistry and jewelry. It has a much higher production cost than the FDM technique.
Digital Laser Processing (DLP)
Digital light processing machines and technology are almost the same as the SLA. The main difference is that the DLP uses a digital light projector to make a single image of each layer at once (or multiple flashes for larger parts), resulting in a layer formed from small rectangular blocks called voxels.
DLP has a faster printing time compared to SLA. That’s because an entire layer is displayed at once, instead of tracing the cross-sectional area with the tip of a laser.
The light is projected onto the resin using light-emitting diode (LED) screens or a UV light directed to the construction surface by a Digital Micromirodrome Device (DMD).
Selective laser sintering (SLS)
The main advantage of this method, between the types of 3D printing technologies, is that it does not need to support the model during its manufacture, avoiding some post-printing treatments and allowing it to handle a high-level project with complex finishing.
This technique allows us to produce parts with a relatively wide range of materials, such as nylon and carbon fiber. It consists of a laser of CO2 that melts small particles of powdered material, thus forming each of the object’s layers. The powder that is not reached by the laser remains in its natural form, and with that, it ends up serving as the support itself.
Another advantage of this method is that depending on the material, and the parts can have high mechanical resistance, allowing it to perform functions that it would not be able to do if printed with another technique. But, as a disadvantage, there is a higher cost of the material and the printer itself.
Direct metal laser sintering (DMLS)
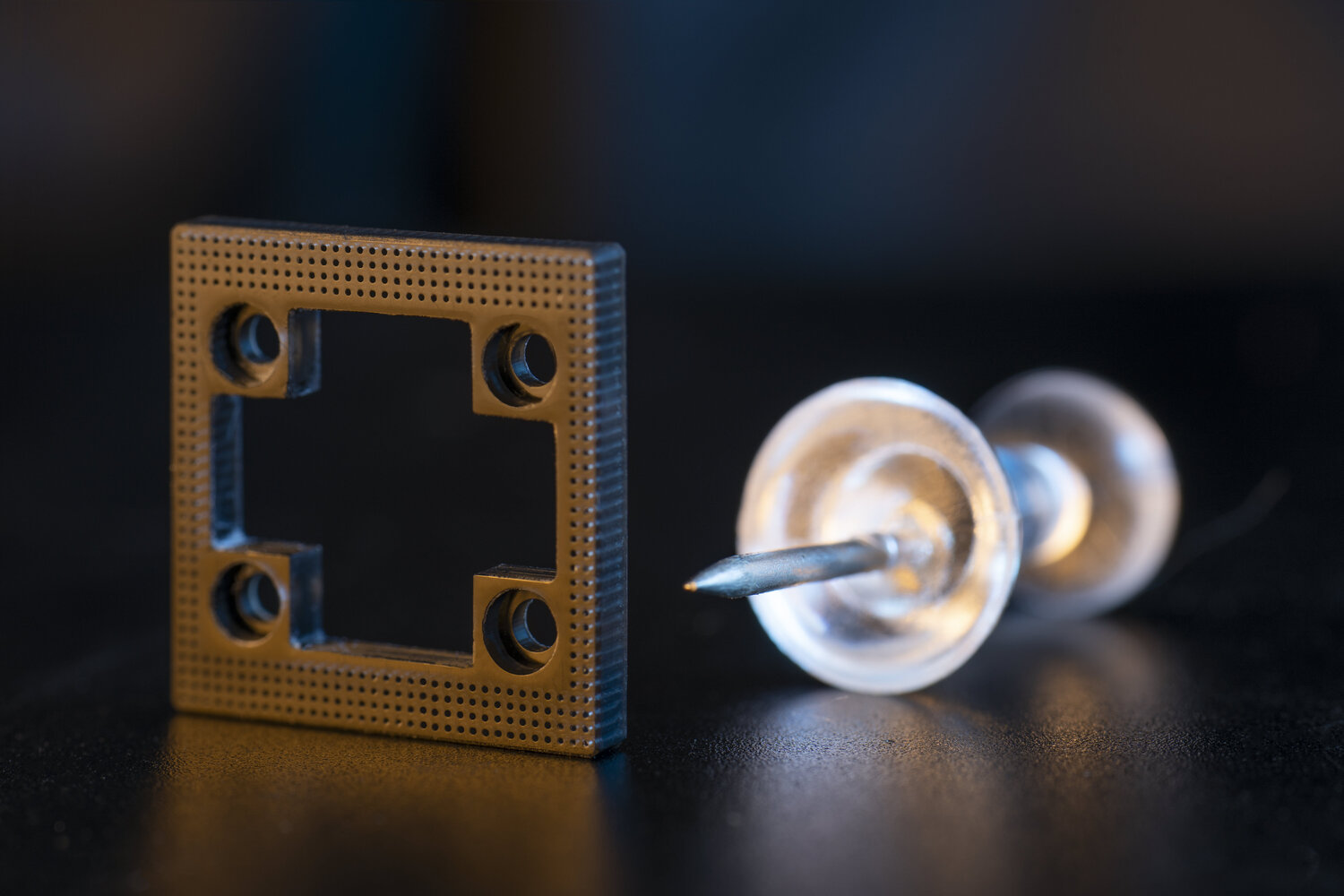
This technique is similar to SLS but uses metals as material. It needs a powerful laser (Yb-fiber laser) that can fuse particles of metals to form the layers of the object. Its great advantage is that it allows us to create complex final parts that are quite complicated to produce in traditional models of manufacture. It has a higher cost of printing (both printer and printed parts). Its often used in few areas of industry, such as aerospace, medicine, and dentistry.
Drop on Demand (DOD)
Drop on Demand (DOD) uses a pair of inkjets. One deposits the building materials, which is normally a wax-like material. The second is used for dissolvable support material. DOD printers follow a planned path to inject material into a point deposition, creating the cross-sectional area of an object layer by layer. It also uses a cutter through the construction area after each layer is designed, ensuring a perfect surface before starting the next layer. DOD printers are generally used to create suitable patterns for lost wax casting or investment casting, and other mold making applications.
Material Jetting (MJ)
Material Jetting (MJ) works in a similar way to a standard inkjet printer. The main difference is that, instead of printing a single layer of ink, several layers are built on top of each other to create a solid piece. The print head injects hundreds of tiny photopolymer drops, and then shapes/solidifies them using UV light. After a layer has been deposited and cured, the build platform is lowered to layer thickness. The process is repeated to create a 3D object. MJ is different from other types of 3D printing technology that deposit, sinter, or cure construction materials using point deposition. MJ machines deposit construction material quickly and linearly. The advantage of in-line deposition is that MJ printers can manufacture multiple objects on a single line, which doesn’t impact on construction speed.
As long as the models are arranged correctly, and the space within each construction line is optimized, the MJ can produce parts faster than other types of 3D printers. Objects made with MJ requires support, which is printed simultaneously during construction from a soluble material. MJ is one of the only types of 3D printing technology that offers versatility, enabling the construction of products made from multi-material and color printing.
Metal Binder Jetting (MBJ)
Yes! It is possible to print metallic materials, too.
Binder Jetting uses powdered base material and a liquid binder. The powder is spread in layers in the development chamber, and the binder is applied through jets, gluing the powder particles. After printing, the final product is a particleboard that is inside the chamber covered by the remaining powder. This dust is removed and can be reused for the next printing.
Sand Binder Jetting (SBJ)
Sand Binder Jetting devices are types of low-cost 3D printing technology for producing sand parts, for example, sandstone or plaster. For color models, objects are manufactured using a plaster-based powder in conjunction with a liquid binder. The printhead first injects the binding agent, while a secondary printhead discharges in color, allowing full-color models to be printed. After the curing process, they are removed from the loose and clean powder. To improve mechanical properties, parts are often exposed to an infiltrating material. There are a large number of infiltrators available, each resulting in different properties. Coatings can also be added to improve the vividness of colors.
Selective laser melting (SLM)
Selective laser melting, or SLM, is sightly different from DLMS, although it is often used interchangeably. However, SLM melts pure metals, while DMLS fuses metal alloys.
SLM is one of the most impressive 3D printing technologies available today and is utilized for rapid prototyping and mass production. The range of metal alloys is fairly extensive. The result has properties equivalent to those manufactured via traditional manufacturing processes.
Electron Beam Melting (EBM)
Unlike other Powder Bed Fusion techniques, EBM (Electron Beam Melting) uses a high-energy beam, or electrons, to induce the fusion between the metal powder particles. A focused electron beam sweeps a thin layer of dust, causing localized fusion and solidification in a specific cross-sectional area. These areas are created to create a solid object. Compared to the SLM and DMLS types of 3D printing technology, EBM generally has a higher construction speed due to its higher energy density. However, things like minimum feature size, dust particle size, layer thickness, and surface finish are typically larger. It is also important to note that EBM parts are manufactured by vacuum, using only conductive materials.
3D printing technologies working with CAD software
Although there are several free CAD programs on the market, not all of them have important features for 3D printing.
Do you know what CAD means?
Computer-aided design (CAD) is a software that designs a project or a product and records all the process. It allows the modeling process by transferring extensive diagrams of a product’s materials, strategies, tolerances, and measurements with particular conventions for the stock in question. What does CAD stand for? It creates either two-dimensional or three-dimensional diagrams, which can be interpreted from any point of view, even from the inside looking out. It works along with some 3D printer technologies CAD is also less-known as computer-aided design and drafting (CADD).
The most important is the ease of interaction and integration with the 3D printing process. Essentially it all depends on the ability to generate 3D models that can be transformed into 3D printing instructions. The simplest way to solve this is to save the model in the format we know as an STL file.
Another important aspect is the creation of mechanical instructions to create 3D objects through additive manufacturing. The printability of the model is also an important feature, especially when it comes to producing or customizing parts. Some platforms create models that will still need to be repaired after printing.
Finally, CAD software for 3D printing must also be easy to use when creating or modeling objects.
Different sectors have already identified in 3D printing a viable alternative. Whether for creating prototypes or final pieces, technology is already a reality for several segments. It is no different for the mechanical industry! The use of 3D printing has facilitated the realization of projects in this sector. So engineers and designers are making the most of 3D modeling software. They are useful for many applications, from simulation to manufacturing processes. There are outstanding software solutions with high-level features that allow you to work on truly technical projects.
We separate several CAD software that we consider it the best ones in the market:
Solidworks
SolidWorks is one of the popular 3D modeling software. SolidWorks Corporation initially developed it, but in 1997 the company was acquired by the French multinational Dassault Systèmes S.A. The software is based on parametric computation. It expresses each spatial variable in terms of an independent variable (or two, in the case of surfaces), thus creating three-dimensional shapes from geometric shapes. In the program environment, the creation of a solid or surface begins with the definition of a 2D model that is then transformed into 3D. SolidWorks has a good range of features, including specific functions for sheet metal, welded construction, and molds. So we can say that software solutions cover many levels of the product development process and provide a continuous and integrated workflow: design, verification, design, communication, and data management. It is considered one of the greatest 3D modeling software for engineers and designers. Since it is a complete tool for creating innovative mechanical models, this 3D software has a friendly interface. It can be used perfectly by engineering students looking for a tool to make mechanical drawings! Despite being a paid software, it has a free trial version without the need to be downloaded. To do this, you only need to create an account and log in to the site.
Autodesk’s Inventor
Inventor software was developed by the Autodesk company and allowed you to create three-dimensional virtual prototypes. The 3D projects generated in this software are functional. The model of an engine, for example, can be animated so that its parts move and rotate, just like the real engine.
Autodesk Inventor also includes the engineering part, not only modeling the parts but also allowing their mechanical behavior to be evaluated, thus going beyond the scope of the main CAD tools.
Version 11 of the product comes with a Dynamic Simulation module. In this module, the mechanism is placed under the effects of acceleration due to gravity and all other forces present in the system. This allows the user to observe and analyze the behavior of his part.
The software can be downloaded in the following languages: Czech, German, English, Spanish, French, Italian, Japanese, Korean, Polish, Portuguese, Slovenian, and Chinese.
It is one of the paid 3D modeling software, but it has an evaluation version. The best thing is that for students, there is also the option of the free version of up to 3 years. So it’s worth downloading and checking!
AutoCAD
AutoCAD is one of the 3D modeling software. It contains tools to assist the development of technical drawings in some areas like architecture, hydraulic, electrical, structure projects, etc., or in mechanical projects designing parts for the industry, among many other types of projects.
Everything that is manufactured or built must first be designed, and most of the drawings are developed in AutoCAD!
So, no matter how much you learn to use the tool and know what AutoCAD is, you must have specific knowledge of the area you intend to work in, whatever it may be.
If it is mechanical, try to understand what makes up a project. Besides, what each part of it is for and, if possible, even see its application. For sure, this simple step will already contribute to your knowledge base.
AutoCAD is a paid software with a free trial version that is available for 30 days after being installed.
It is worth remembering that these are some of the 3D modeling software that allows you to perform excellent 3D printing projects. But not only that, since most have a wide range of tools available.
Although all are paid, they have free trial versions for a certain period. So it is very worthwhile to use even if the test options are to learn more about how each can be used.
SolidFace
We consider our CAD software the best 3D modeling software, and we tell you why. Check it out!
If you need a CAD or a 3D Modeling software, SolidFace is both. It has a FREE license with several features that will improve your modeling abilities and offer the best printing experience. Check some advantages and understand why We consider it the best option for you.
Data Management: Don´t have trouble saving a project. Solidface ALWAYS saves the lastest data. You and your team to be free to work and control a project without losing it in the middle. Every single adjustment will be captured and recorded. Also, you can undo and redo by your decision at any time. It has never been so easy. It also has branching and merging spaces that enable you to develop other projects in parallel while working on a current one.
Teamwork Collaboration: we consider teamwork collaboration is the key to success. So we offer you space where you may perform 3D modeling projects together and seemingly with your friends, work colleagues or other users. In SolidFace, everyone works in real-time and can modify it freely, editing, controlling, shaping, designing, etc.
3D Part Library: Enjoy over 100 million parts and hundreds of leading components from different manufacturers and distributors.
3D assemblies: Solidface is a powerful ally for you to design high-level and detailed projects, working along with other hardware, projects, or libraries (such as a3D rendering software. It also has movement simulations as crash and collision test. Our dynamic parametric capabilities and collaboration module majority solve the problem with missing files and broken links.
Drawing: creates drawing with parametric reference for modeling features in no time, that can be edited in a very simple and interactive way. This is a 3D module fully integrated with all parts and components. Also, it is very flexible. Enables to import and export DWG, DWT, and DXF file formats.
Customizable interface: Work it in your way. Change themes, colors, positions, and toolbars as you want. Divide your graphics workstation up to 16 view windows, allowing a multi-visualization of project details or different parallel designs.
Quick Support: Any questions or doubts? No problem! Request our support directly on our website. We offer free support for entry-level doubts via e-mail.
Free Tutorials: We feel a strong connection to many designers and engineers who have difficulty acquiring the best CAD software. At SolidFace, we truly want you to improve your skills and become a master at modeling and 3D printing. So if you want some good content, check out our Youtube channel. We have several videos and tutorials to help you. Always free and available
The global market is passing through a big and strong technological revolution, aiming to do more with less, be efficient, and be sustainable. In the additive manufacturing business, several paths have emerged as the use of 3D printing technology. Many ways to develop a new product were created using techniques like extrusion, binder jetting, sintering, and melting. But, along with all these methods, it also requires 3D modeling skills. We separate some CAD alternatives that we believe its the best workstation on the market.
Solidface 3D came with one big purpose: give flexibility and teamwork collaboration for those who want to master your modeling abilities and become a skilled worker on using 3D printing technologies.