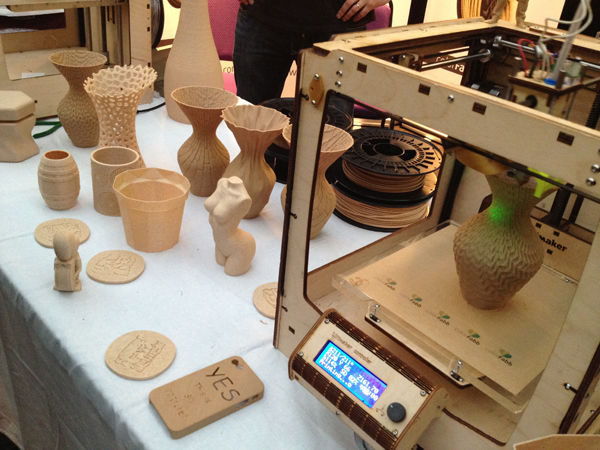
3D printing materials have developed a lot in recent years. Several companies have already identified the potential and are investing in innovations, applying new technologies and functions to printers, and developing new products.
Many companies are becoming a reference in the development of 3D printing materials, with laboratory and manufacturing structures focused on these products worldwide. However, given the options, choosing the best filament for each project can raise doubts. In this post, we will present the available materials and the ways to find the most suitable for your project. Check out! In this guide, we separate some pros and cons of each filament to choose the best one for your project.
Today, the 3D printer filament allows you to create objects with completely different characteristics. With the same printer, you can create from decorative pieces to objects used in large engineering projects. They can have high mechanical and chemical resistance as well as they can have a rustic appearance. See some of the main 3D filaments:
PLA Filament

PLA (polylactic acid) is produced from renewable sources and is not harmful to your health or the environment when the parts are discarded. Easy to print material, allowing use in open or closed printers, with or without a heated table. Due to its low contraction, it is indicated for large and technical parts, with controlled dimensions, and parts that will be exposed to abrasion efforts due to its high surface hardness compared to other materials. Its colors are brilliant and make it possible to print very vibrant pieces.
PLA is a primary material to use if you are a 3D printing student; it is easy to grasp, one of the cheapest and creates pieces that can be used for various applications. Derived from gatherings such as corn and sugarcane, PLA is renewable and, most importantly, biodegradable. It also has sweet aroma during printing so you can take your mask off if you are far from the printer (but safety first, always remember that)
Pros: Low cost, Easy to handle (strong and stiff), flexibility (good accuracy) and durability (great lifecycle)
Disadvantage: Low heat resistance, not indicated to be exposed in sunlight.
ABS Filament

ABS is a material widely used in industries. Its temperature resistance and impact absorption make it a suitable material for 3D printers. Also, its opaque color has a pleasant look for parts that need less brightness.
A very attractive feature of ABS is the ease of finishing after printing. Because it is a material of low surface hardness, it becomes abrasive and easy to sand, in addition to having acetone as a solvent.
If the part printed in ABS has a more opaque aspect, the acetone finish gives more shine and manages to correct some imperfections that can be generated. But remember that acetone must be pure and handled with care as it is very volatile.
ABS filament comes in a wide range of colors. Please pay attention when using ABS because there is concern about the toxicity of ABS fumes when it melts. To solve this, you can use PLA. The ABS’s printing temperature reaches 220°C to 250°C, so it is highly recommended to use a heated printing bed and a confined room with cooling resources to control the heat of the material and prevent any chance of warping. Also, several 3D printing materials degrade with high and constant air humidity, storing it in vacuum bags or containers.
Pros: low cost, heat and wear resistance, easy handling, and smooth finishing.
Disadvantage: Heavy warping, Support required (heated bed or heated chamber), bad smell and shrinking risk (lower accuracy)
PETG Filament
PETG filament is the noblest material on our list. Because, in addition to being a very mechanically, chemically, and temperature resistant material, it is a material with high printing ease. Like PLA, it can be used in open or closed printers, with or without a heated table. It also features the ease of printing the PLA combined with the properties of ABS, which is great for 3D printing. Besides, it has high chemical resistance, which allows it to be used on parts that will suffer interference with some reagent. It does not have a significant warp, making it possible to print large pieces. In addition to the filaments already mentioned, some others also have excellent characteristics. We can call them special filaments. PETG is the initials to a Glycol Modified version of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET), often used on plastic bottle manufacturing. There are many variations of this material in the market, including PETG, PETE, and PETT. The tips in this article will apply to all of these PET-based filaments.
Pros: Quality finishing, insignificant warping, No bad smell while printing process.
Disadvantage: Can produce waste on the surface from stringing.
Flexible Filament

Flexible filaments, often referred to as TPE (Thermoplastic Elastomers or TPU (Thermoplastic polyurethane), are recognized for their elasticity allowing the material to stretch and bend easily.
As the name suggests, this material is elastic in nature, allowing the plastic to be stretched and flexed easily. One of the special 3D printer filaments produced in our factory is the flexible filament. This product can expand the use of the 3D printer in parts that need good flexibility.
The flexible filament has very interesting applications, such as the creation of insoles, seal rings, bracelets, and other things. However, to print this material perfectly and avoid problems, it is necessary to observe your printer.
If there is excessive clearance between the tractor and the extruder, the flexible filament can bend and interrupt printing. It is best to talk to the machine or material manufacturer to assess the possibility before purchase.
Pros: Flexibility and softness, Long life cycle, and good impact resistance.
Disadvantage: Difficult to print, easy to create blobs and deformation.
Nylon filament
Nylon, a well-known family of synthetic polymers used in many industrial applications, is one of the champions in 3D printing. Compared to any other 3D printer filament, it reaches the first place in the ranking when considering the set of resistance, flexibility, and durability.
Another particular feature of this 3D printer filament is that you can dye it before or after the printing process. The downside is that nylon, like PETG, is hygroscopic, which means it absorbs moisture. Don’t forget to keep it in a ventilated and dry place to guarantee good quality prints. In general, there are many gradations of nylon, but among the most used as filament for the 3D printer are 618 and 645. You can take advantage of nylon’s strength, flexibility, and durability to create functional prototypes and mechanical parts (such as hinges, buckles, or gears).
Pros: resistance, flexibility, durability
Disadvantages: usually expensive; sensitive to moisture; requires a high temperature on the table and the print nozzle.
PC – Polycarbonate
In addition to being one of the stronger 3D printer filament on this list, polycarbonate is much durable and resistant to both physical impact and heat, being able to withstand temperatures up to 110ºC. It is also transparent, which explains its use in commercial items such as bulletproof glass, diving masks, and electronic device screens. Although it can be used in similar situations, the PC should not be confused with acrylic or plexiglass, shaken or broken under pressure. Unlike these two materials, the PC is moderately flexible (although not as much as nylon, for example), which allows it to bend until eventually deformed.
The PC is a filament for a hygroscopic 3D printer, capable of absorbing moisture from the air. So, don’t forget to keep it in a ventilated and dry place to guarantee good quality prints.
Due to its physical properties, the PC is a 3D printer filament ideal for parts that need to maintain strength and form on high-temperature environments, such as electrical, mechanical, or automotive components. You can also try to take advantage of its optical clarity in lighting projects or on electronic screens.
Pros: extremely strong; resistant to heat and physical impact
Disadvantages: sensitive to moisture; requires a high printing temperature
Metal Filament
Suppose you’re looking for a different look for your prints, which is a little more bulky and shiny. Well, for that you can use metal. Like the wooden filament, the metal filament is not metal. It is a mixture of powdered metal with PLA or ABS. But this does not prevent the results from having the appearance and texture of the metal. Even the weight is similar to that of metal, as mixtures tend to be denser than pure PLA or ABS.
Bronze, brass, copper, aluminum, and steel are just some of the varieties of metal filament available on the market. If you’re interested in a specific look, don’t be afraid to polish, transform, or stain metal items after printing.
You will possibly need to change your print nozzle right after printing with metal, as the grains are somewhat abrasive and increase wear.
Pros: offers a metallic appearance; ideal for both functional and aesthetic models
Disadvantages: difficult to print; highly abrasive for the print nozzle
PLA Flex filament
The PLA Flex filament was created to facilitate the printing of a flexible filament. As shown in the previous topic, to print with flex, there should be no excessive clearance between the tractor and the extruder. In the case of PLA Flex, this is not necessary. PLA Flex is a little more rigid than the normal flexible, and this makes printing much easier. Then, you will be able to print with the same parameters as the PLA (including print speed!), Except the extrusion temperature, which in the PLA Flex should be between 230 and 245 ° C, also different from the normal PLA.
Pros: easier and faster to print.
Disadvantage: Not fit with some process.
HIPS filament
Soluble filament, or HIPS, is a mixture of polystyrene and rubber material. As it dissolves in the d’ limonene solution, it is often used for support material, such as with ABS, eliminating the need for removal using abrasives, cutting tools, or any other things that leave your impression with a lower surface finish. Not only is it great for supporting your ABS prints, but it also more stable and lighter than ABS, making it a great alternative for parts that would end up getting wasted out or used in applications that can serve from the lighter weight.
Pros: Low cost, resistance to water and impact, highly recommended to lightweight manufacturing, dissolvable by d-Limonene.
Disadvantage: ventilation required and Support (heated bed or chamber),
Wood filament

Wood filament is a special material produced with wood fibers and other components like dust, cork, wood powder with PLA. It consists of around 30% of wood particles, but it may change depending on the brand. The presence of these particles provides the 3D printed parts the appearance of real wood. This filament is also less abrasive than other composite filaments such as carbon-fiber filled and metal filled since wood particles are much softer. Some wood-like filaments on the market only contain wood coloring. Still, there are no actual wood particles, so they typically have a very different look and feel, like a synthetic kind.
Pros: Smooth and appealing finish, pleasant smelling
Disadvantage: Tendency to stringing, clogs on the smaller nozzles over time requiring a larger size.
Tritan HT Filament
This is the filament with the highest resistance and hardness that was designed for use in 3D printers. It is a durable copolyester and is resistant to high temperatures (100ºc), pressure and alkaline, acidic, and water solutions.
Another important point is its use in advanced 3D printing projects. It has an excellent adhesion between layers and resistance to traction. It is much more durable and flexible than PLA and ABS and has great adhesion to the table, which implies the use of a table heated around 110ºc.
Pros: Very durable and is more flexible than conventional PLA or ABS; it has low contraction and low or no warping. Ideal for large prints.
Disadvantages: More expensive.
Talking about the material characteristics
With the advancement of technology, 3D printer materials developed are multiplying. Each day the need to meet specific user requests increases. However, initially, the filaments were developed for users with a general pattern of parts.
However, the more technical and detailed the parts become, the need for materials grows to support the requirements of each project, such as temperature, mechanical resistance, chemical resistance, etc.
Below is a chart that exemplifies the mechanical differences of the main materials used in 3D printers.
How to choose the ideal material?
Now that you know the main filaments for 3D printers, let’s give you four tips to choose the ideal material for your project.
1. Check what the application is planned for
First of all, you need to analyze what conditions your manufacturing process will have. Some questions need to be answered, such as:What is the objective of this produced part? What conditions (internal and external) will it be exposed to?
Will it work on which temperature? Any contact with reagents? These are some examples that will assist you in defining the best material for your printing. Application analysis also serves to know how a part will meet your needs and if what costs will be involved. Sometimes, the part you want to manufacture has no specific need and can be printed with cheaper material. Other times it will need to be very specific on choosing the appropriate material and conditions. This thinking can greatly increase the final results (or cost) of the project.
2. Choose the best 3D modeling software (CAD)
Among hundreds of CAD software for 3D modeling, you need to understand which one has the necessary resources to deliver the best result for your project, right? So, to stay on top of the subject, let’s better explain what CAD is, how it works, and then some examples of CAD software for engineers and designers.
CAD software (from Computer-Aided Design) allows engineers and designers to create realistic models of parts and assemblies. Technical drawings and 3D digital models are made through this software, facilitating the later conception of the project. These digital models can then be manufactured using 3D printers and 3D printing materials, quickly reaching a physical form, identical to digital. CAD software can also be used to run simulations in the virtual environment. Some 3D modeling software has a wide range of parameters that simulate resistance to force or temperature, before any physical model has been created, allowing a much faster and cheaper workflow.
There is a wide range of CAD software with different packages available, serving different sectors depending on your specifications:
Solidworks – Industry-standard software, used for modeling parts and assemblies. Includes simulation features, some drawing module, and assembly tools.
AutoCAD – is a 2D and 3D CAD software package. It is used by a wide range of industries, architects, project managers, engineers, graphic designers, and many other professionals.
Fusion 360 – Fusion 360 is popular with engineers, designers, and educators. It is similar to Solidworks, with the addition of integrated manufacturing tools and sculpting tools. It is also free for students, enthusiasts, amateurs, and startups.
Sketchup – Sketchup is easy to use entry software with more basic features. They are often used for applications such as architectural models and interior design.
Solid Edge – Solid Edge offers solid modeling, assembly, and 2D functionality for mechanical designers. Solid Edge is a direct competitor to SolidWorks, PTC Creo, and Autodesk Inventor.
SolidFace is a FREE 2D/3D CAD software with many advantages like data management (automatically saving and support all data formats), teamwork collaboration at real-time, 100 million parts and components, drawing and assembly module, and much more.
3. Check the characteristics of your printer
As we previously said, some materials like PLA and PETG can be printed on any printer. However, ABS is mainly indicated for closed and heated table printers. If your printer does not have these characteristics, this may be a limitation in material choice. So, be aware of this point and not buy material that your printer cannot work with. If you don’t choose your 3D printer yet, it is important to consider your goals for choosing the best option. Here is an option:
Tevo Michelangelo: Considered an entry model, Tevo Michelangelo has a great cost-benefit compared to other 3D printers. With an estimated cost of U$500.00, the model has a resolution of 0.1 mm – which we can consider relatively good – and a maximum speed of 120ms. Tevo Michelangelo also has an aluminum structure, capable of supporting PLA and TPU filaments. In short, you can meet the needs of a beginner in 3D printing with ease.
4. Check material availability
If you have already analyzed the application of the part and checked if your printer can work with the material, it is now time to check the filament’s availability. Some companies that supply filaments work only with basic materials. That is, you will find a range of options between materials and colors. Today, the company manufactures and supplies PLA, ABS Premium, Flexible, PLA Flex, Wood, PETG, and HIPS (soluble). Also, a very large amount of colors is offered, reaching almost 20 variations according to the material.
5. Estimate the budget
Many people are using the 3D printer to offer printing services. But for that, it is necessary to calculate all the costs involved. You must take the following points into account: adequacy of the 3D model if necessary; finishing work; input; printing time; investment in the machine; waste rate; spent electrical energy; profit margin.
Conclusion
The correct choice among the different types of filaments available on the market is extremely important to guarantee the quality of the printed material and the quality of the final product. Paying attention to what is indicated for your printer and having the appropriate CAD software, its success is guaranteed.
Do you want to know more about the types of filaments used in 3D printing and their main characteristics?
Check it out on our blog and stay on top of all our new productions and ideas!